What is an NFT?
The NFT abbreviation stands for Non-fungible token – a non-interchangeable, or even simpler, unique token. This is a digital asset that is provably unique. NFTs can be used to represent both tangible and intangible items.
They first emerged back in 2017 on the Ethereum blockchain platform. However, unlike bitcoin, ether, and other cryptocurrencies, NFT is a one-of-a-kind object with its own price.
To make things easier, let`s take an apartment as an example. Imagine that you are buying an apartment. Information about the purchase is recorded in the state register including the data about the new owner of the apartment, transaction date, etc. Basically, that`s how NFTs work. They certify the object of digital space belongs to you. And just like with an apartment, you can sell it to anyone at any price. In fact, you normally sell not the object itself but only a unique token that references it.
NFTs can be whatever you want, from a cute picture with kittens to the first Instagram post. Basically, an NFT is a digital analogue of a document establishing your right to an object. It contains information about the owner and the set of rights provided by the token.
NFT Types
Digital Art
NFT art is the most popular way in which many online artists buy and sell digital art. It is not unique but limited, creating scarcity and an authenticity sense that makes it especially valuable.
In February 2021, Mike Winkelmann, also known as Beeple, sold his digital work “Everydays: The First 5000 Days”. It became the first piece of digital art to be auctioned by Christie’s. A few days earlier, a GIF animation of Nyan Cat was sold at an online auction for $590,000.
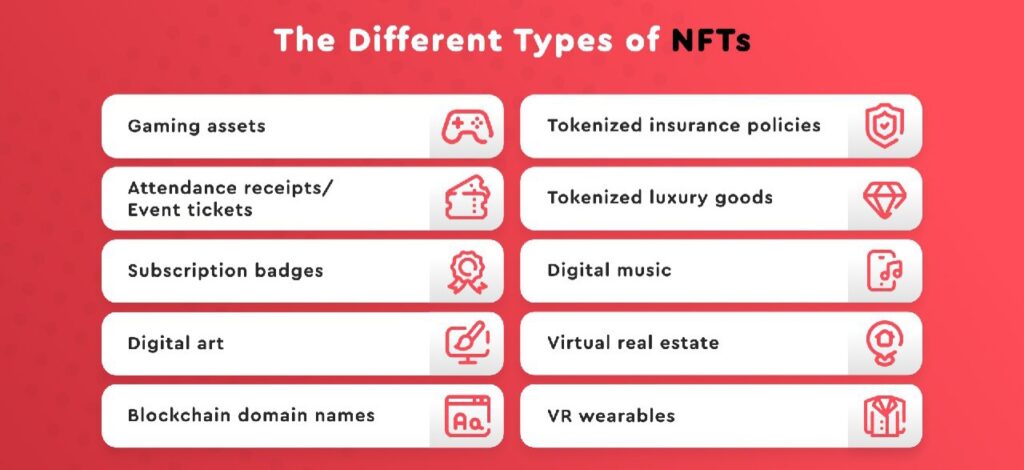
Attendance receipts/Event tickets
Event tickets can also be tokenized as NFTs. Event organizers, especially those who sell tickets for VIP seats, can make good use of this category. Tokenization of these tickets enables participants to easily authenticate their tickets and identity.
In the ticket sales system, event organizers can use the blockchain to make any number of tickets and distribute them through their websites and apps. They can also encode everything they need in NFT – from the ticket image and its ID to the method of checking and selling this ticket (for example, at a fixed price or through an auction).
When users buy an NFT ticket, it will be stored in their wallets such as bitcoins or ether, which can be accessed from their mobile devices.
Gaming assets
NFTs can be used to represent in-game assets like digital land plots. Game developers are implementing NFT to allow players to win virtual in-game items such as digital swords, shields, and other collectibles. Tokenization of game items into digital assets has also simplified the transfer of tokens among players or different games through a specialized NFT blockchain registry.
CryptoKitties was an early successful online blockchain game where players adopted and exchanged virtual cats. The empedded monetization of NFT within helped developers raise $12.5 million investments.
Virtual real estate
NFT-land is an owned digital space on the metaverse platform. Popular virtual land projects include Decentral, The Sandbox, and Axis Infinity. Non-interchangeable tokens are perfect for representing land rights, since each of them is unique and allows you to prove digital ownership. Owners can use NFT-lands for advertising, communication, games, work, and more.
Typically, landowners purchase NFT-land to host online events, post content, or gain in-game benefits. Major brands and celebrities, including Adidas and Snoop Dogg, have already invested in their own NFT lands.
Digital music
NFTs provide a great opportunity for music artists to earn on their content. Apart from the music albums and its digital cover, musicians can sell unlockable content, a unique link that can be opened only once. It can provide the rights to receive an exclusive box set, to create copies, get income from future sales or broadcasts, etc.
To aggregate and sell tokens, you can use such marketplaces as Musicon, Raible, Nifty Gateway, and OpenSea. They offer artists various earnings options and provide sales verification.
NFT Benefits
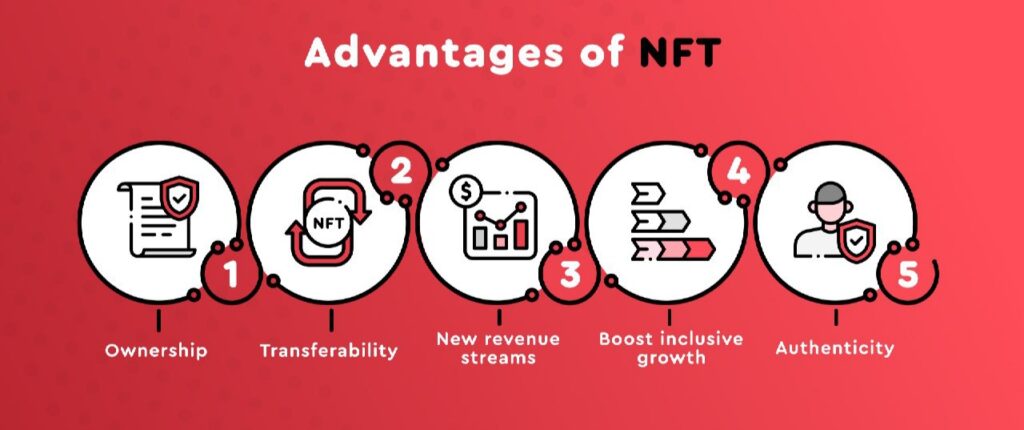
Ownership
NFTs prove the ownership of unique digital assets, which represent the results of creative activity, using blockchain technology. NFT is a unique token stored in the blockchain, it is inseparable and exists in the singular form. This way, users can make sure the digital asset belongs to them and therefore seamlessly dispose of it.
Transferability
You can easily transfer your NFT to another crypto wallet. While some worry about safety of NFT transferring, it is absolutely secure. In particular, cold storage hardware wallets are the most reliable tool to store and transfer your tokens. They provide the most security for your digital assets since your sensitive data is stored offline. Moreover, all your data is password-protected which provides an additional layer of security.
New revenue streams
With the help of NFTs, both businesses and individuals can get a new earning source. Income can be obtained from saling NFT as digital property by concluding smart contracts on the NFT auction site, as well as from the placement and sale of NFT objects within various metaverses.
NFT risks and challenges
Legal & Regulatory
Since the NFT market is not regulated by special legislation, there are some problems of its legal protection.
Firstly, it`s challenging to identify the user of the auction NFT platform, who violated the exclusive rights to the token by copying the file and thus placing their own token. The problem results from the low requirements for user identification when registering them on the auction site, as well as the fact that transactions on such platforms are made in cryptocurrency (ethers).
Secondly, the creation of a new token with a copy of a file from another token is characterized by the lack of effective protection mechanisms. It is practically impossible to prove that the token belonging to the user is the original unlike the copy created by the other user.
Thirdly, there is the problem of responsibility of NFT marketplaces for offenses committed by users within their platforms. The solution to the problem may be the creation of a centralized organization at the international level, which will issue licenses for the activities of auction sites, as well as monitor all existing sites for the presence of illegally borrowed tokens.
Cyber Security & Fraud Risks
The security threats of non-interchangeable tokens are in many ways similar to the risks associated with any cryptocurrency. Just like interchangeable coins, NFTs can be the object of theft. If cybercriminals get access to the user`s wallet, they will be able to transfer the tokens stored to themselves. Considering the decentralized and one-sided nature of blockchain transactions, it will be very difficult to return the stolen tokens.
There are also some risks that typical only for non-interchangeable tokens. These include the possibility of acquiring a counterfeit copy of a digital asset. Indeed, since images, video files, audio recordings, and other virtual objects are easily copied, nothing prevents fraudsters from converting a duplicate of the original work into NFT.
Smart Contract Risk & NFT Maintenance
NFTs are created through a minting process including the conlustion of a smart contract stored on the blockchain. There are several ways how cybercriminals can hack a DeFi (Decentralized Finance) network and steal a large amount of crypto. Recently, the most-renowned DeFi protocol named Poly Network was attacked by hackers, and $600 million were stolen in this NFT theft. This resulted from inadequate security of smart contracts.
Valuation
The major problem people encounter in the NFT market is the uncertainty in determining the NFT price. Currently, it is determined by such factors as creativity, uniqueness, scarcity of the buyers and owners, and more. However, NFT prices can considerably fluctuate since there is no fixed standard for any particular type of NFT.
Users can’t define the factors that might drive NFT price. Therefore, the price fluctuations remain constant, and evaluation of NFT becomes a real challenge.
Statistics
While NFTs help businesses turn their companies into full-fledged digital spaces, the global NFT market size is swiftly growing. In 2020, its capitalization amounted only for $340M. However, in just a year, it hit nearly $25B, increasing its valuation by over 70 times. In 2022, the market capitalization is projected to exceed $35 billion. Moreover, it is expected to reach $80 billion in 2025.
The key driver of the NFT industry is rising use of NFT in supply chain and logistics. NFTs can prevent businesses from counterfeiting helping in tracing the product movement across the supply chain, and ensure originality. This can be helpful for numerous supply chains for high-end fashion businesses.
Enterprise NFT use cases
Music & Social Media
Music marketplaces have already been crowded with both novice crypto investors and digital artists who are trying to sell their NFTs. Many famous musicians are actively selling their works in the form of tokens.
The showcases of NFT marketplaces now look more like 3D galleries than streaming service charts. However, if a musician pays great attention to the visual aspect of their works, they may be in demand at NFT auctions.
Digital fashion
The Fashion-NFT concept includes clothes, shoes, jewelry, accessories, and much more – everything that can be worn in VR or gaming realities. These digital wearables are used today not only as speculative tools and collectibles but also for personalizing avatars in GameFi, in the AR environment and for superimposing on real objects in the process of photo and video shooting.
However, now the main use of digital wearables is found in Decentraland-level decentralized game worlds. This NFT field is just starting to gain popularity. Its use is limited by the difference between a real accessory and its digital counterpart, which is still noticeable. However, with the improvement of image processing technologies and developments in the field of artificial intelligence, the differences will completely disappear.
Goods & Supply Chain
Blockchain technology can also be useful in the logistics industry. Transparency and immutability of the system guarantee the reliability of information in the supply chain: it is important for buyers to know the way their purchase is supplied.
What makes NFTs special is that they represent unique items. They can be used to track goods – view data about their origin, route and location of the warehouse.
There are many hypothetical ways to introduce NFT into the process of delivering goods but for each of them it is necessary to apply the same system at all stages of the supply chain. Due to the large number of participants in the process, it can be quite difficult to implement this idea.
Metaverse
This digital universe is conceived as an alternative to the real world, where digital currencies (cryptocurrencies) and NFT (non-interchangeable tokens) represent an environment since users can buy products or services in it.
Los NFT are unique digital assets that certify the originality of a work or a specific article. On the Decentraland virtual reality platform, several plots of digital land have exceeded half a million dollars.
The popularity of NFT in Metaverses has grown as it represents the main means by which people can acquire various objects in the universe through their avatars, such as art, houses, cars and others. As a consequence, the sale of tokens in the Metaverse has increased significantly in recent months, given its huge popularity.
Conclusion
The popularity of NFTs continues to grow, which means we will see more and more different options for using non-interchangeable tokens. Today, many ways to use NFT are still at the stage of an idea or a small project, so some of them may be impractical or unpopular. However, in the field of digital art and collectibles, NFTs are already playing an irreplaceable role.



