You know that 42% companies fail due to the lack of demand for their product? In order to avoid this, you need an MVP. It will help you allocate resources properly and test the product viability before launch.
What is an MVP?
A minimum viable product (MVP) is a basic version that covers the product’s fundamental components, features, and targets as well as the core needs of customers. This stage allows entrepreneurs to try themselves on the market spending a minimal amount of resources.
Typically, MVP includes a brief idea description and basic set of functions. Although the product is minimally equipped, it still has to meet market’s needs and wants, solve their problems, and demonstrate its value. Despite its ‘rawness’, an MVP should provide a clear picture of what the final product is supposed to look like.
In a nutshell, an MVP means creating a basically featured product that can be offered to customers. Then, you observe the market`s reaction, adjust the version to users` requests, and create a full-fledged product based on the feedback. This way, the company minimizes risks to fail and increases chances to reach demand.
Why do you need an MVP?
Frequently, companies spend years trying to understand whether or not the product will take off. As a result, they end up with nothing since the product turns out to be useless on the market. With the help of an MVP founders can validate their hypotheses and get a quick response from consumers without spending extra time, money, or efforts.

MVPs provide direct and indirect financial advantages which allow businesses to:
get a feedback from the target audience in order to refine the product before entering a larger market;
identify the product`s strengths and weaknesses;
see if the market actually needs the product;
release a product faster and get profit even before finishing its development;
convince investors of more serious funding for finalizing the product;
save costs associated with product development.
How to develop an MVP?
To launch a minimum viable product, it is necessary to go through the following stages.
Formulate the task
Each product serves to solve a certain problem, and it’s not about making a profit. A customer-oriented approach is essential when creating an MVP. So think of the reasons why your users might need the product. Having a clue, you will get an idea of the product aim and its value.
Identify the audience and highlight its segment
Focusing on the needs of a wide audience when designing an MVP is a flawed strategy. Narrowing the target audience allows you to more accurately develop the future product.
To do this, you need to draw a portrait of the “ideal” user, a person who will buy your solution without hesitation and will be satisfied with its capabilities. Typically, it includes information about the user’s age, education level, income, habits, interests, and hobbies. These details are crucial to understand how well the product will satisfy their needs and will help you later, at the stage of advertising and promotion.
Examine your competitors
Even if you have come up with something really new, there will be companies that are already operating in the chosen industry. Their experience, advantages and disadvantages should be carefully identified. Find out what their market share is, why customers come to them and what makes them unique. These details will help you adjust the MVP.
After a fundamental analysis of the business idea, it’s time to look at the future product from the user’s point of view. A customer journey map reflects the order of actions that the user performs in order to achieve their goal, for example, to purchase a product or rent a parking space.
This map should not only be as short as possible but also simple and convenient. Having thought through how the user interacts with the future application, you will understand at what stage to provide additional information, where to add a hint and how to optimally design the interface.
Elicit the main functions to implement and calculate the MVP volume
No matter how large the conceived project is, for MVP it is necessary to list and prioritize its functions. When creating a Minimum Viable Product, give a preference to those features that are directly related to the main purpose.
Additional functions will only confuse users and reduce the reliability of the results of the business idea research. They can be added after the deployment of the MVP, collection, and analysis of primary feedback.
Select the appropriate methodology and develop an MVP
Having determined the scope, order, and direction of work, you can start developing a minimum viable product. The result chiefly depends on how exactly the development process will be built. For MVP, it is important to use one of the iterative approaches to development such as Lean, Scrum, Kanban, extreme programming. All of them enable you to establish regular release of updates, improve the product on the go as feedback is being received.
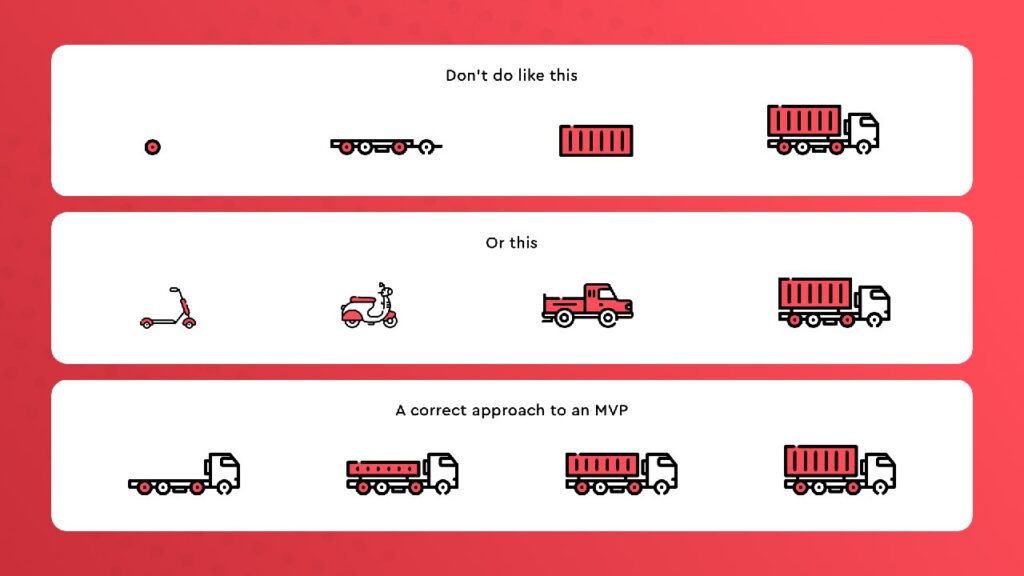
Test the product
An MVP requires regular testing throughout its development. Alpha testing is carried out within the team but beta testing will require the help of outside specialists. The main aim of testing is the technical improvement of your MVP. Before the release, the product must work so seamlessly that technical problems do not prevent users from evaluating its functionality.
Launch
Now it is necessary to collect, save, and analyze feedback, covering the statistics from numerous aspects. This is the principal goal of an MVP. The data collected with the help of MVP will allow you to understand whether the project has prospects, help generate new ideas, and develop a product development strategy based on facts.



